Understanding Mastectomy: Symptoms, Diagnosis, and Surgical Options
Understanding Mastectomy: Symptoms, Diagnosis, and Surgical Options
A mastectomy is a surgical procedure that involves the removal of all breast tissue from a breast, primarily to treat or prevent breast cancer. This procedure can be a life-altering event for many, and understanding the symptoms leading to a diagnosis, the surgical options available, and the process itself is crucial for those facing this journey.
Symptoms Leading to a Diagnosis
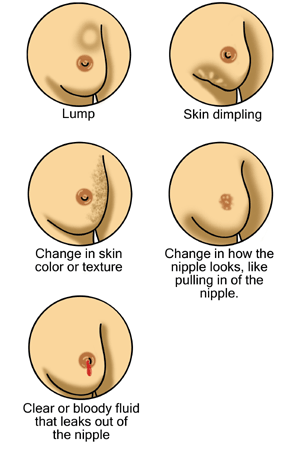
The path to a mastectomy often begins with the detection of symptoms that may suggest breast cancer. These symptoms can include a lump or thickening in the breast, changes in the size, shape, or appearance of a breast, changes to the skin over the breast such as dimpling, a newly inverted nipple, or peeling, scaling, crusting, or flaking of the pigmented area of skin surrounding the nipple (areola) or breast skin.
Diagnosis of Breast Cancer
If these symptoms are present, a healthcare provider will recommend tests and procedures to diagnose breast cancer, which may include a mammogram, ultrasound, magnetic resonance imaging (MRI), or a biopsy. If breast cancer is diagnosed, a mastectomy may be recommended as a treatment option, especially if the cancer is in its early stages or if there's a high risk of recurrence or spread.
sours of photo: Lectorio
Surgical Options
There are several types of mastectomy procedures:
- Simple (or total) mastectomy: Removal of the entire breast, including the nipple, areola, and skin.
- Modified radical mastectomy: Combines a simple mastectomy with the removal of lymph nodes under the arm.
- Skin-sparing mastectomy : Most of the skin over the breast is left in place, with only the breast tissue, nipple, and areola removed.
- Nipple-sparing mastectomy: Similar to skin-sparing, but the nipple and areola are left intact.
The choice of procedure depends on various factors, including the stage and type of cancer, size of the tumor, patient's health, and personal preferences. Some procedures, like skin-sparing and nipple-sparing mastectomies, are designed to facilitate immediate or subsequent breast reconstruction, offering cosmetic benefits and aiding in the psychological recovery process.
**Recovery and Reconstruction**
Post-mastectomy recovery involves managing discomfort, caring for the surgical site, and gradually resuming daily activities. Pain and swelling are common, and drains may be placed to remove excess fluid. Physical therapy may be recommended to regain strength and flexibility.
Breast reconstruction can be performed at the same time as the mastectomy or at a later date. Options for reconstruction include implants or using tissue from other parts of the body. The decision to undergo reconstruction is personal and can be influenced by many factors, including the individual's health, the type of mastectomy performed, and the need for additional cancer treatments.
**Conclusion**
A mastectomy is more than just a surgical procedure; it's a complex decision that involves understanding the risks, benefits, and emotional impact. It's essential for individuals to discuss all aspects of this treatment with their healthcare team to make informed decisions that align with their health needs and personal values.